A number of Japanese companies and organisations have established a ‘Promotion Council for Zero Emission Chargers for Ships’, aiming for more widespread use of standardised shore-to-ship power stations –
The companies behind the Council are e5 Lab, Marindows, e-Mobility Power, CHAdeMO Association, Japan Ship Technology Research Association, Mitsubishi Shipbuilding and Development Bank of Japan.
In October 2020, Japan declared a goal for carbon neutrality by 2050, and expressed its aim to reduce emissions by 46% by 2030 compared to 2013 levels, and aim for even further reductions to 50%. In a joint declaration between Japan and the US in April 2021, both countries agreed to cooperate on Carbon Neutral Ports (CNP). In Japan, port areas are pivotal in the international supply chain, with over 99% of exported and imported goods passing through them. These areas are at the heart of coastal industrial zones, where power plants, steelworks, chemical industries, and others, responsible for about 60% of the country’s CO2 emissions, are concentrated. Intensive efforts towards decarbonisation in these port areas are seen as effective and necessary to promote Japan’s carbon neutrality by 2050. In this context, shore-to-ship power supply, which involves supplying electricity from land to ships, is attracting attention as a concrete measure to reduce CO2 emissions. Approximately 40% of CO2 emissions in ports come from diesel generators on docked ships. Moreover, these generators not only emit CO2 but also cause a significant impact on the surrounding environment by emitting noise, vibration, NOx, SOx and particulates. Harmful emissions from docked ships can be reduced at the source through the development of onshore power infrastructure, leading to improvements in global and local environments. The Council, in line with the government’s policy and as a world-first initiative involving the member companies, has recognised the effectiveness of shore power) for ships to promote decarbonisation in maritime and port areas and the expansion of renewable energy use.
Taking into account the various issues experienced in the earlier stages of the ship power supply business, the participating members will play their respective roles and through an All-Japan collaboration centred on the seven companies mentioned above, will aim to develop and maintain a strategic ecosystem for zero emission chargers for ships, and to strategically engage in efficient operations and effective utilisation. This is expected to lead to improved user convenience, an increase in the number of ships using the service, the independence of the ship power supply business, and the further development of chargers. Ultimately, this can lead to zero emissions from ships in port areas, the spread of electric-powered ships, the expansion of renewable energy use, and improvements in global and local environmental issues.
The first phase, by 2025, will see prototype standardised universal zero emission chargers for ships installed in Hanshin Port and Keihin Port, which are international strategic ports where domestic and foreign freight and ships are concentrated. Following this, the plan is to expand these chargers to ports, fishing ports, marinas nationwide, and overseas. Moreover, City of Kobe, Port and Harbor Bureau and City of Yokohama, Port and Harbor Bureau are participating in the Council as observers.
The specific initiatives of the Council are:
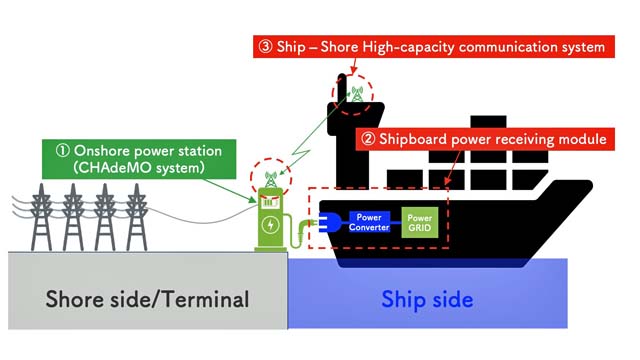
- Development of a standard universal zero emission charger system for ships, which will consist of three elements offering a standardised specification that transcends company boundaries.
a. Onshore power station (standardised charger and billing system)
b. Shipboard power receiving module (standardized and modularized hardware and software)
c. High-capacity communication between ship and shore (standardised high-capacity communication system within the port) - Surveys and recommendations on the establishment of standards and rules
- Creation of social implementation projects to promote diffusion
- Information collaboration between participating companies
- Mutual utilisation of zero emission chargers between participating companies
- Public relations and promotional activities to promote the diffusion of zero emission chargers
- Cost reduction through joint procurement
- Content creation for ‘Zero Emission Charger × X’
- Building a sustainable ecosystem, including reuse.